Cyber threat intelligence
Cyber threats continue to evolve continuously, and organizations must protect themselves from them. Organizations can defend against attacks proactively and mitigate potential damage by continuously gathering and analyzing information about potential threats.
In addition, Organizations can prioritize their defenses and allocate resources effectively through cyber threat intelligence. If they understand the specific threats that are most likely to affect them, they can focus on those that need the most attention. defenses get adequate Cyber threat intelligence allowing organizations to stay one step ahead of potential attackers and reduce the likelihood of a successful breach.
An organization’s cybersecurity strategy depends heavily on cyber threat intelligence. Organizations can proactively defend themselves against attacks and mitigate attackers that have compromised a system or network, potential threats, and defenses, and allocate resources accordingly. Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is the collection and analysis of information about cyber threats and adversaries. It is used to create threat models that provide an ability to make informed decisions for
- cyber threat preparedness
- Prevention
- Detection
- Response actions
against various existing, emerging, and predicted cyber threats or attacks. The CTI program helps senior business leaders make strategic, operational, and tactical decisions on existing, emerging, and predicted cyber threats or attacks to the organization. It also helps organizations identify and mitigate various business risks by converting unknown threats into known threats and recommending advanced and proactive defense strategies. CTI is both a product (report, presentation, or message) and a process (collect, process, and produce).
The organization develops their Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) strategy based on their business requirements and risk level. CTI helps reduce the effectiveness of existing, emerging, and predicted cyber threats or attacks faster and better, it also helps in recommending actionable strategies and tactics that can be implemented to help mitigate cyber risk, it helps organizations identify adversarial opportunities for attack and proactively mitigate cyber risks. CTI Provides high-level situational awareness to management and executives to understand significant threats to protect critical assets and business processes. CTI Provides analyzed Threat Actor Campaigns that help security teams shift their investigation from specific indicators to attack TTPs, speeding up their investigations. CTI requirements are that the products should be
- Objective
- Timely
- Accurate
- Actionable
Cyber Threat Intelligence requirements need to come top-down, NOT bottom-up. Cyber Threat Intelligence works best on top of an already functioning security program which sits on top of a mature IT organization. Actionable Threat Feeds require Quality IOC’s (low volume, high quality) over Quantity IOC’s (high volume, low quality). General Requirements for CTI Success: A Solid Planning and Direction document, Priority Intelligence Requirements (PIR’s), and a Mature, well-functioning IT organization.
Source:
Cyber threat intelligence – Wikipedia
Threat intelligence – Wikipedia
Video:
The Cycle of Cyber Threat Intelligence
The different type of life cycles in cyber threat intelligence
The Cyber Threat Intelligence Lifecycle is the process of gathering, analyzing, and disseminating information about cyber threats in order to protect an organization from potential attacks. The process typically involves several stages, such as collection, analysis, and dissemination, and may also include activities such as threat hunting and incident response.
The Indicator Lifecycle
is the process of identifying and tracking specific indicators of compromise (IOCs) associated with cyber threats. This process typically includes stages such as identification, verification, and dissemination of indicators and ongoing monitoring for changes or updates to the indicators.
The Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)
Lifecycle is the process by which an attacker establishes and maintains a prolonged, undetected presence within a target organization’s network. This typically includes reconnaissance, weaponization, delivery, exploitation, and post-exploitation.
The Ransomware Lifecycle
is the process by which a ransomware attack is carried out and the victim’s response to it. This process typically includes stages such as initial infection, encryption of files, ransom demand, and payment or recovery of files. Working in Cyber Threat Intelligence is all about defeating cognitive biases to ensure an objective and accurate intelligence product. Security personnel often use their experience as a full bias to quickly come to conclusions during investigations. All Threat Analysts have biases (those biases can be good, effective, and quick, but they also can cloud judgment. Cognitive
Biases or fallacies
refer to systematic errors in thinking that can lead to incorrect judgments or decisions. Some common types of biases include:
Correspondence Bias
is the tendency to assume that a person’s behavior is consistent with their personality or character rather than the situation they are in.
Confirmation Bias
is the tendency to look for, interpret or remember information in a way that confirms one’s prexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
Self-Serving Bias
the tendency to attribute one’s successes to internal factors and one’s failures to external factors.
Belief Bias
is the tendency to judge the validity of an argument based on the believability of its conclusion, rather than the logical strength of the argument itself.
Hindsight Bias
is the tendency to believe, after an event has occurred, that one would have predicted or expected the event to happen.
Anecdotal Fallacy
is the tendency to believe that a personal experience or testimonial is more significant than statistical data.
Appeal to probability
is the tendency to believe that an event is more likely to occur if it is more desirable or more consistent with one’s own beliefs.
Counter-bias strategies
are methods used to reduce or eliminate the influence of biases in decision-making processes. These biases can come in many forms, such as cognitive biases, social biases, or algorithmic biases.
Decision theory
is a branch of mathematics that studies the decision-making process, with a focus on identifying the best decision in a given situation.
Game theory
is a branch of mathematics that studies strategic decision-making, particularly in situations where multiple individuals or groups are involved.
Behavioral economics
is a field that combines psychology and economics to study how people make decisions. It examines how cognitive biases and other factors affect economic decision-making.
Cognitive psychology
is a branch of psychology that studies the mental processes involved in perception, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Machine learning
is a field of artificial intelligence that focuses on building systems that can learn from data and make decisions without explicit programming.
Human reliability engineering
is a field that focuses on understanding and improving the reliability of human performance in complex systems.
Overall, these fields provide a variety of techniques and methods that can be used to understand and counteract biases in decision-making, and to improve the reliability and effectiveness of decision-making processes. Below we show you how to find actionable threat intelligence, Threat, and how to make the Threat Assessment.
Threat intelligence equations
- Actionable Threat Intelligence = Objectively written + Timely delivery + Accurate facts + Actionable Recommendations.
- Threat = Opportunity + Capability + Intent.
- Attack = Motive (Goal) + Method + Vulnerability
- Threat Actor Campaign = Actor Name + Observed Attacks/Intrusions + Actor TTP’s + Key indicators (IOC’s or IoA’s).
- Threat Assessment = Confidence levels + Analysis + Evidence + Source References.
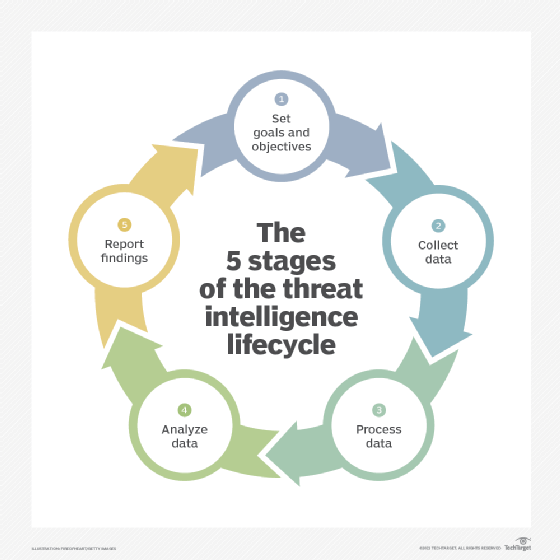
Source:
The 80/20 of the Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) Domain Knowledge
STIX (Structured Threat Information Expression)
Set of tools used to represent cyber threat intelligence in a standardized, structured way. It allows organizations to share information about cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and other related data in a way that is easy to understand and use. STIX consists of a set of schemas, objects, and patterns that the attackers may use information that can be represented, as well as a set of tools for creating, validating, and manipulating STIX content.
TAXII (Trusted Automated eXchange of Indicator Information)
It provides a framework for sending and receiving information about cyber threats in a secure, standardized way. TAXII includes specifications for transporting information and authenticating and authorizing the parties involved in the exchange. It also includes services for managing and distributing cyber threat intelligence, including subscribing to feeds of information and requesting specific data types.
CybOX (Cyber Observable eXpression)
A language for representing cyber observables or pieces of evidence related to cyber threats or incidents. It allows organizations to describe and share information about specific artifacts or indicators observed in their systems or networks. CybOX includes a set of objects and patterns that define the various types of cyber observables that can be represented and a set of tools for creating and manipulating CybOX content. It is designed to be used with STIX, allowing organizations to represent more complex cyber threat intelligence in a structured way. Identifying vulnerabilities in the organization’s systems and networks, cyber criminals use the latest tactics and techniques to exploit these vulnerabilities.
STIX, TAXII, and CybOX help combine indicators of compromise (IOCs) and indicators of attack (IOAs) because they provide a standardized, structured way to represent and share this information. By using these tools and languages, organizations can more easily share information about potential threats and vulnerabilities with external partners and authorities. This can help to improve situational awareness and allow organizations to take more proactive measures to protect themselves and their assets.
IOCs (indicators of compromise)
are evidence that may indicate that an attacker has compromised a system or network. These could include hashes of malicious files, IP addresses or domains associated with an attack, or other artifacts left behind after an attack. By using STIX and CybOX to represent these IOCs in a structured way, organizations can more easily share and analyze this information and use it to identify and mitigate potential threats.
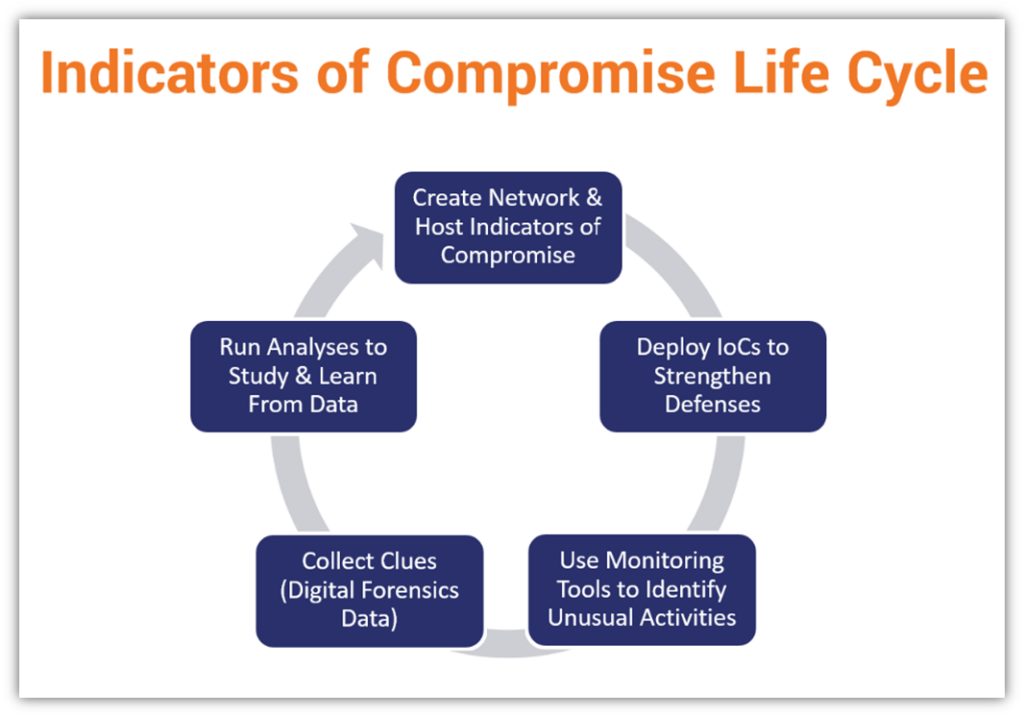
Source:
Indicator of compromise – Wikipedia
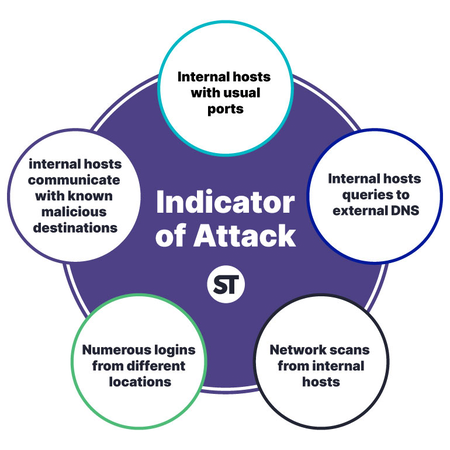
IOAs (Indicators of Attack)
on the other hand, are specific actions or techniques that attackers may use to compromise a system or network. These could include things like specific exploits or vulnerabilities that are being exploited or particular tactics or techniques that the attacker is using. By using STIX to represent these IOAs in a structured way, organizations can more easily understand and analyze the methods used by attackers and take steps to protect against them.
TAXII is particularly useful for combining with IOCs and IOAs because it provides a framework for exchanging this information securely and efficiently. By using TAXII, organizations can share IOCs and IOAs with one another in a way that is authenticated and authorized, ensuring that the information being shared is reliable and trustworthy. This can be particularly important for cyber threat intelligence, where accurate and timely information is critical for effective defense.
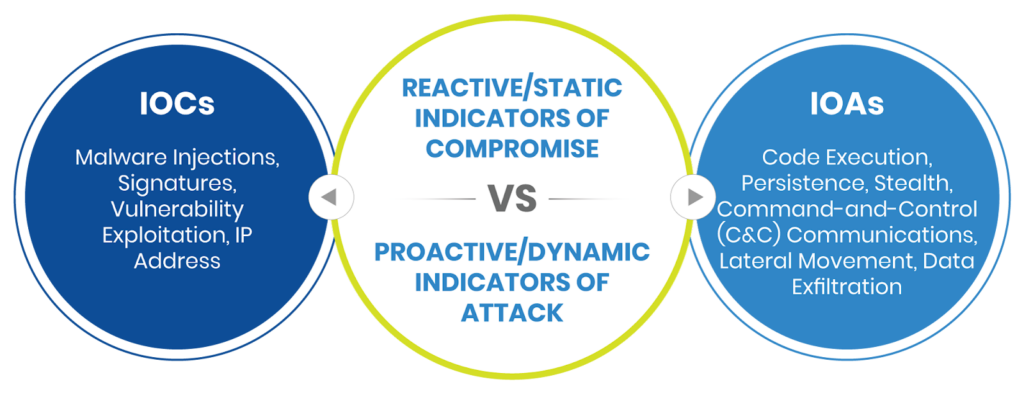
Source: